
What is a Roth IRA?
A Roth IRA is a type of individual retirement account that allows you to contribute money after taxes. The key benefit of a Roth IRA is that your money grows tax-free inside the account, and when you withdraw it, it’s also tax-free if you meet certain requirements. This makes it a popular option for those looking to save for retirement.
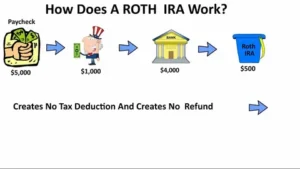
How Does a Roth IRA Work?
You contribute to a Roth IRA using after-tax dollars, meaning there’s no immediate tax deduction. However, if you meet specific conditions, withdrawals are tax-free. While the money is in the Roth IRA, it grows without being taxed.
Contribution Rules and Limits for a Roth IRA
Both traditional and Roth IRAs have annual contribution limits, which are combined across all IRA accounts. For the 2023 and 2024 tax years, the annual contribution limits are:
- 2023: $6,500 ($7,500 for those 50 or older)
- 2024: $6,500 ($7,500 for those 50 or older)
Contributions for a given tax year can be made up until the tax filing deadline (April 15 for most years), without extensions. To contribute to a Roth IRA, your income must fall below certain limits, which vary by filing status.
Who Qualifies for a Roth IRA?
To contribute to a Roth IRA, you must have earned income (from employment or self-employment). Other forms of income, like interest or investment income, don’t count. The income limits for contributing to a Roth IRA are based on your Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI).
Income limits for 2023 and 2024 differ based on your filing status:
- Married Filing Jointly or Qualifying Widow(er): Income limit for Roth IRA contribution.
- Single, Head of Household, or Married Filing Separately (if not living with spouse): Income limits.
- Married Filing Separately (if living with spouse): Income limits.
Spousal Roth IRA
If you’re married, you can open a Roth IRA for a non-working spouse. To qualify, you must file jointly. This allows both spouses to contribute the maximum amount to their Roth IRAs if desired. In 2024, that’s $7,000 each, plus an additional $1,000 catch-up contribution for those 50 and over.
The working spouse must have earned income, and both spouses must stay within income limits for the Roth IRA.
Other Ways to Fund a Roth IRA
- Rollovers: You can roll over funds from other Roth accounts, such as a Roth 401(k) or Roth 403(b), without worrying about income limits or taxes.
- Roth Conversions: You can convert assets from a traditional IRA or 401(k) into a Roth IRA. While you’ll have to pay taxes on the conversion, it allows you to contribute more than the usual IRA limits.
- Backdoor Roth IRAs: High earners who can’t contribute directly to a Roth IRA can use a “backdoor” method. This involves contributing to a traditional IRA and then converting it to a Roth IRA. Taxes may apply depending on the amount.
- Mega Backdoor Roth IRA: If your employer offers this option, you can contribute more than the typical 401(k) limit by making after-tax contributions and then converting those to a Roth IRA.
Pros and Cons of a Roth IRA
Pros:
- Tax-Free Withdrawals: If certain conditions are met, you can withdraw your contributions and earnings tax-free.
- No Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs): Unlike traditional IRAs, you don’t have to take distributions at a certain age.
- Tax-Free Growth: Your money grows without being taxed during the time it’s in the account.
- Inherited Roth IRA: If you inherit a Roth IRA, you can withdraw the funds tax-free if the account holder met the five-year rule before passing away.
Cons:
- No Tax Break Upfront: Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, so you don’t get a tax deduction now.
- Income Limits: Your ability to contribute may be limited if you earn too much.
How to Open a Roth IRA
You can open a Roth IRA through brokerage firms like Fidelity, Vanguard, and Schwab, or through robo-advisors. Many banks and credit unions also offer Roth IRAs, though investment options might be limited. The process generally involves completing forms and providing personal information. You can also name beneficiaries for your account.
Withdrawals: Qualified vs. Non-Qualified
You can withdraw contributions from a Roth IRA at any time without taxes or penalties. However, there are different rules for earnings and other withdrawals.
Qualified Withdrawals
To be considered “qualified,” withdrawals must meet the following conditions:
- At least 5 years have passed since your first contribution.
- You are at least 59½ years old, or the distribution is due to disability or death, or it’s for a first-time home purchase (up to $10,000).
Non-Qualified Withdrawals
Non-qualified withdrawals may be subject to taxes and penalties. However, contributions are always tax-free and penalty-free. Earnings may be taxed and penalized unless exceptions apply, such as:
- Disability
- Death of the account holder
- Certain medical expenses or higher education costs

Roth IRA vs. Traditional IRA
- Roth IRA: Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, and withdrawals are tax-free if qualified. No required minimum distributions (RMDs).
- Traditional IRA: Contributions are made with pre-tax dollars, giving you an upfront tax deduction. However, withdrawals are taxed as ordinary income, and RMDs apply.
Roth IRAs also have income limits, while traditional IRAs have income limits only for pre-tax contributions if you’re covered by an employer-sponsored plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much do you need to open a Roth IRA?
There is generally no minimum required to open a Roth IRA, though some custodians may have their own minimum deposit requirements.
Can you withdraw money from a Roth IRA?
Yes, you can withdraw your contributions anytime without taxes or penalties. Withdrawals of earnings may be subject to taxes or penalties if they don’t meet the qualified distribution criteria.
Do you pay taxes on a Roth IRA?
Your contributions are made after-tax, so there are no taxes when you contribute. If you meet the requirements for qualified withdrawals, your earnings will also be tax-free.
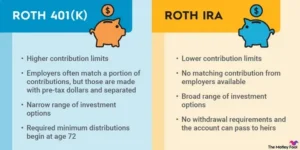
What is better: a Roth 401(k) or a Roth IRA?
Both have advantages. A Roth 401(k) has higher contribution limits and no income restrictions. However, Roth IRAs offer more investment flexibility and generally better options for self-directed investments.
In summary, a Roth IRA is an excellent choice for many retirement savers due to its tax-free growth and withdrawals. It’s important to understand the contribution limits, income requirements, and rules for withdrawals to make the most of your account.



